The history of Ottawa, as elsewhere in Canada, has included brothels. It was common practice to group several whorehouses with a tavern next to them. In Ottawa and Quebec, for example, such brothel districts operated in the downtown area.
A common accompaniment to the relationship for money was gambling and alcohol. Such a combination made brothels the most profitable businesses in the first half of the 19th century. Ottawanka will tell you more about their history.
The heyday of brothels
At the turn of the century, with the development of transcontinental railroads, there was a mass migration. Moreover, in the West, most of the migrants were single men or those who had temporarily left their families at home. Thus it was a perfect environment for brothels to heyday.
Such establishments were located near railway stations. Interestingly, the authorities in those days took hardly any drastic steps to influence the situation or close the establishments in any way. Their stance was one of patience since eradicating this practice was impossible.
Brothel owners have faced difficulties since the 1890s. It was all due to legal repression, as well as widespread street prostitution. When we compare the number of women who offered love for money during World War I, their number was high due to low employment opportunities, but, already during World War II, the level of prostitution decreased several times.
Generally speaking, in Canada, prostitution used to be considered not a crime and neither were brothels.

Brothels in different eras and their transformation
- Pre-Confederate Era. The authorities controlled prostitution until 1867, wherein offenders included women of easy virtue and street revelers. Brothel owners, as well as their employees, were prosecuted by law. During that period, arrests were of a more unpredictable, chaotic order.
- Victorian era. Subsequently, the authorities introduced more complex provisions. Their purpose was to protect women, as well as children and brothel owners. The law also applied to pimps. Women were forbidden to sell love for money until they turned twenty-one. In 1892 the Criminal Code was adopted, stipulating search warrants if suspicion arose. For the next 28 years, the laws relating to this area only improved. In the 1920s, the Social Purity Movement faded, with the next 50 years of no public comment on the development of this area of the sex industry.
- Propaganda and debate. The development of street prostitution in residential neighborhoods in Canada became a matter of public concern, which led to a renewed debate in the 1970s and 1980s. In 1983, a Special Committee was created to report on this concern. For example, the Street Prostitution in Canada report by the Canadian Centre for Justice Statistics in 1992 recorded more than 10 thousand incidents that were precisely related to prostitution. About 95% of the crimes were related to intimacy, while about 5% were related to pimping and rudeness.
According to some estimates, an approximate portrait of the majority of brothel workers was young and single women from 22 to 25 years old who started working in these establishments from 16 to 20 years old. Of these, 30 to 70% had children.
Interestingly, a 1998 survey shows that over 7% of Canadian men have bought love for money at least once in their lives.
Major changes
Therefore, during the debate, the Committee creation resolved the situation and introduced changes to the Criminal Code.
- Street prostitution, as well as brothel activities, were no longer subject to the status of an offense.
- Liability for prostitution began to extend not only to women but also to men.
- It was intended to protect women and men from being bought by others.
- In 1988, harsh punishments were imposed on pimps who solicited young people for labor, as well as on clients of underage female workers and brothel workers.

A historical tour through brothels
So the population of Ottawa and Canada in general recollects the following:
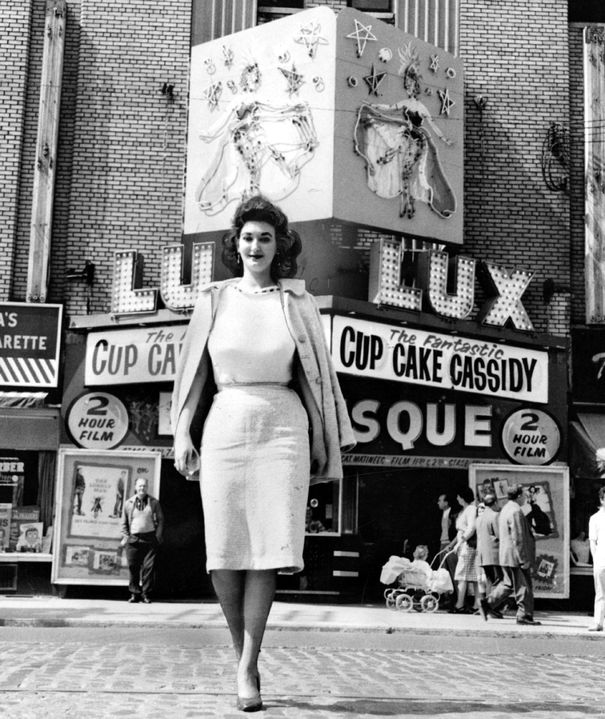
- Strip dancing. In Toronto, for example, there were such clubs as the Lux Burlesque Theatre al College Street to Brunswick Avenue and the Flyers’ Club.
- Reforms. They tried to save sex workers. For example, reformers sent women to do housework, work as cooks, laundresses and other similar jobs.
- Where is freedom? Women were thrown into women’s prisons for charges related to brothel work, pregnancy outside marriage and public drunkenness. The principles of reform called for correction through work and prayer.
- It is impossible not to mention the story of Albert. Born in Ontario, Madame was arrested in Winnipeg. She looked like a businesswoman and possessed powerful political and economic connections. The woman herself, selling her love for money, repeatedly explained that it was the only way to be financially independent outside of marriage.

Modern age
Since the 1990s, the debate regarding the activities of brothels has changed its perspective. Sex worker lawyers have become concerned with other issues:
- Women’s and men’s fears related to HIV and AIDS.
- Maintaining this category in migration.
- The development of sex workers’ rights.
- Community education, as well as launching programs that make any discrimination against sex work impossible.
- Improving the safety of brothel workers.
Already in 1997, the Criminal Code was amended accordingly. In 2003, the creation of the Federal Standing Committee on Justice and Human Rights became a significant milestone. After that, a series of laws were passed to increase safety to protect sex workers.
In present-day Ottawa, under Bill C-36, prostitution, like the operation of brothels, is illegal. In other words, the purchase of sexual services is a violation of the law.
Looking through arrest records, it is worth mentioning over 20 brothels, as well as other key places, that played a pivotal role in the development, heyday and transformation of the sex industry. If, at first, brothels operated “blindly,” then further on, their transition became noticeable. There were also changes in regulations and laws, while the safety of workers in this area was given more importance.

